
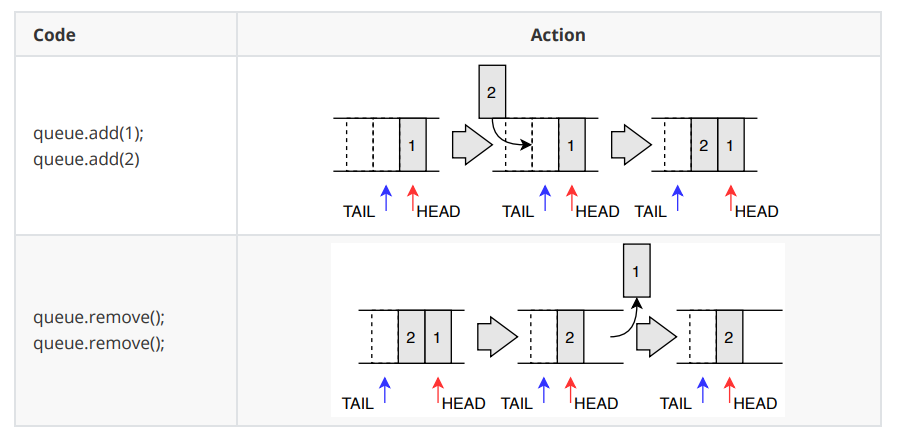
- FIFO(First-In-First-Out)으로 먼저 저장한 데이터가 먼저 나오는 구조를 가집니다.(선입선출)
- 즉, 저장된 데이터중 가장 앞에 있는 데이터만 접근 가능함을 나타냅니다.
- 음식점에서 주문을 위해 줄을 서고, 가장 앞에서부터 주문함으로 예로 들 수 있습니다.
ArrayList
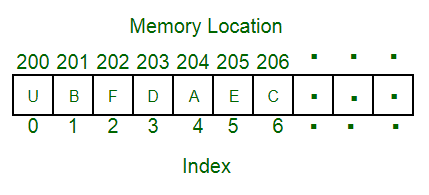
- An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations.(배열은 연속되는 메모리 공간에 값을 저장한다.)
- The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together.(같은 타입의 값을 저장한다.)
- This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array).
📌출처: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/array-data-structure/?ref=shm
[Queue Interface]
package arrays;
public interface Queue {
public boolean isEmpty();
public void add(Integer element);
public Integer element();
public Integer remove();
public int size();
}Basic Operations on Queue:
- enqueue(): Inserts an element at the end of the queue i.e. at the rear end.(끝에 요소 추가)
- dequeue(): This operation removes and returns an element that is at the front end of the queue. (맨 앞에 요소를 삭제하고 돌려준다.)
- front(): This operation returns the element at the front end without removing it.(삭제 없이 맨 앞 요소를 돌려줌)
- rear(): This operation returns the element at the rear end without removing it.(삭제 없이 맨 뒤 요소를 돌려줌)
- Empty(): This operation indicates whether the queue is empty or not.(queue가 비어있는지 확인 메소드)
- size(): This operation returns the size of the queue i.e. the total number of elements it contains.
📌출처: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/queue-set-1introduction-and-array-implementation/
[ArrayList를 이용한 Queue 구현]
package arrays;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class ArrayQueue implements Queue{
final int defaultSize = 100;
Integer[] elements;
int head;
int tail;
public ArrayQueue() {
this.elements = new Integer[this.defaultSize];
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.head == this.tail;
}
@Override
public void add(Integer element) {
//if(elements[this.tail-this.head+1] > element[])
this.elements[this.tail] = element;
this.tail++;
}
@Override
public Integer element() {
//맨 앞에 있는 요소를 삭제하지 않고 돌려준다.
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return this.elements[this.head];
}
@Override
public Integer remove() {
// 맨 앞에 있는 요소를 삭제한 후 돌려준다.
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
Integer value = elements[this.head];
elements[this.head] = null;
this.head++;
return value;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return (this.defaultSize + this.tail-this.head) % this.defaultSize;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder line = new StringBuilder();
int node = this.head;
while (node != this.tail){
line.append((line.length()!=0 ? " ":"")+this.elements[node]);
node++;
}
return line.toString();
}
}- isEmpty()
- 큐에 데이터가 없으면 head와 tail이 같을 것이기 때문에 이를 사용한 메소드이다
- add()
- tail에 입력받은 자료를 넣어준다.(맨 뒤에 자료를 넣는 형식)
- tail을 하나 증가시켜주어야 다음 자료를 받을 수 있다.
- element()
- 큐가 비어있을 땐 값을 돌려줄 수 없기 때문에 이를 확인해 예외처리해준다.
- 맨 앞에 있는 요소를 삭제하지 않고 돌려준다.
- remove()
- 큐가 비어있을 땐 값을 돌려줄 수 없기 때문에 이를 확인해 예외처리해준다.
- Integer형 지역변수를 생성해 현재 head에 해당하는 값을 넣어주고 head에 해당하는 자리에 있는 값을 null로 처리해 참조 해제해 가비지처리를 해준다. (이는 메모리 누수가 있을 수 있는 문제이기 때문에 처리해주는 것이 좋다.)
- 맨 앞의 head를 삭제해서 돌려주었기 때문에 head를 +1 증가시켜준다.
- 해당 값을 돌려준다.
'Back-End > 백엔드 관련 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백엔드 과정][자바 기초] - 큐 구현하기 (3.DoubleLinkedList를 이용한 구현) (0) | 2022.09.06 |
|---|---|
| [백엔드 과정][자바 기초] - 큐 구현하기 (2. LinkedList를 이용한 구현) (0) | 2022.09.06 |
| [백엔드 과정][자바 기초] - 스택 구현하기 (2.LinkedList를 이용한 구현) (0) | 2022.09.06 |
| [백엔드 과정][자바 기초] - 스택 구현하기 (1. ArrayList를 이용한 구현) (0) | 2022.09.06 |
| [백엔드 과정][자바 기초] - hashCode와 equals 그리고 TreeSet과 HashSet (0) | 2022.08.31 |