
커맨드 패턴(Command Pattern)
1. 목적
요구사항(요청, 명령)을 객체로 캡슐화시킨다.
이를 이용해서 다른 요구사항을 지닌 클라이언트를 매개변수화 시킬 수 있다.
요구사항을 큐에 넣거나 로그로 남길 수 있으며 작업 취소 기능을 지원할 수도 있다.
2. 문제
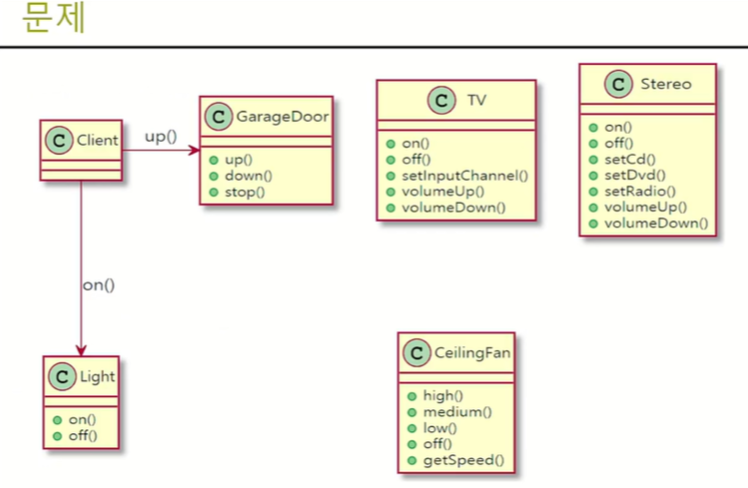
홈오토메이션용 리모콘
사용하려는 객체가 많고, API가 서로 다른 경우(퍼사드 패턴을 사용해도 될거 같지만 다른 경우로 커맨트 패턴을 사용)
- 차고문 up()
- 전등 on()
- Tv pressOn()
예: 홈오토메이션용 리모컨 개발하는데, 차고문, 전등, Tv, Stereo, 에어컨 등 사용해야 하는 객체가 너무 많고 서로 다른 명령들로 구성되어 있다.
3. 커맨드 패턴의 분리란?
커맨드 패턴의 경우엔 요구하는 객체와 그 요구를 받아들이고 처리하는 객체를 분리시킨다.
리모콘 API에서 리모컨 버튼이 눌렸을 때 호출되는 코드와 특정업체에서 제공한, 실제로 일을 처리하는 코드를 분리시키는 것이 필요하다.
리모콘을 눌렀을 때 실제 무슨 일을 하는지를 몰라도 된다.
4. 커맨드 패턴의 요소
| 요소 | 설명 |
| 이름 | 커맨드(Command) |
| 문제 | 사용 객체의 API가 서로 다른 문제가 있다. |
| 해결방안 | 실행과 요청(버튼을 누르는 것)을 분리시킨다 |
| 결과 | (작은) 클래스가 많아지지만, 객체 사용에 필요한 복잡성을 제거하고 감춘다. (함수 이름이 동일해진다.) |
5. 커맨드 패턴 클래스 다이어그램
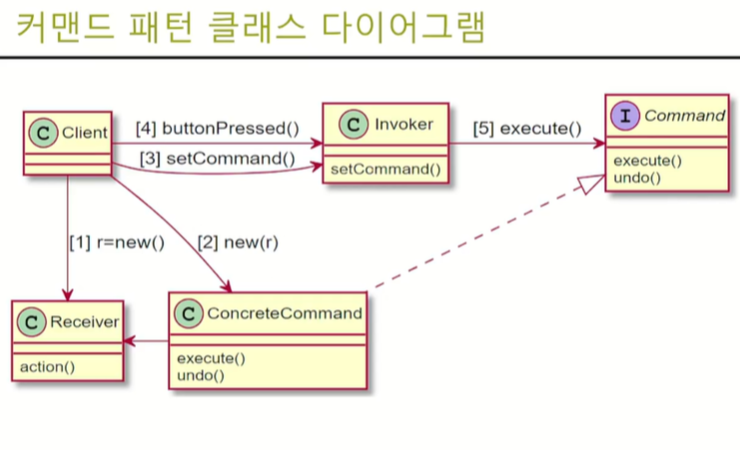
<요청과 실행을 분리>
| Object | 설명 | 레스토랑 | 리모콘 |
| Client | 커맨드 객체 생성 | Client | 리모콘 버튼의 기능을 인지하고 버튼을 누른다 |
| Command(커맨드) | 어떤 Receiver를 실행할 지 연결 | Order | 버튼에 실제 사용 객체를 연결해 놓는다. |
| Invoker | 주문을 받아서, 실행하기 위해 Command 인터페이스를 연결 | Waitron | 리모컨 버튼을 누르면 기능을 실행한다. |
| Receiver | 실제 명령을 수행한다 | Chef | Tv, 전등 같은 실제 객체 |
6. 설계(역할)
Command
- Receiver를 알고 있고 Receiver의 메소드를 호출
- Receiver의 메소드에서 사용되는 매개변수(Parameters)의 값들은 Command에 저장된다.
- 예: Command, ConcreteCommand
Receiver
- 실제 명령(Command) 수행
- 예: Light, GarageDoor
Invoker
- 요청을 받아서, 요청을 실행하기 위해 Command 인터페이스를 연결
- Command 인터페이스만 알고 있고, 실제 Command가 어떻게 실행되는지 모른다.
- 예: 리모콘(RemoteControl)
Client
- 무엇을 요청할지 결정하고, 요청 Command를 Invoker에 넘긴다.
- 예: main( ) 함수
커맨드 패턴 VS 퍼사드 패턴
- 둘은 비슷해보이지만 다르다고 한다. 크게는 퍼사드는 덩어리를 합쳐주는 역할이고 커맨드는 분리를 목적으로 사용한다고 한다
- 또한 퍼사드의 경우엔 역할들을 모두 알고 숙지하고 있어야 하지만 커맨드의 경우엔 몰라도 된다고 한다.
package CommandPattern;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class CalcGUIV1 extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
final static int WINDOW_WIDTH = 400;
final static int WINDOW_HEIGHT = 300;
final static int COMPONENT_HEIGHT = 40;
final static int BUTTON_WIDTH = 50;
String[] buttonText = { "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7",
"8", "9", "+", "-", "*", "/", "=" };
JButton[] buttons = new JButton[buttonText.length];
Calculator calculator;
Dimension displayDimension = new Dimension(WINDOW_WIDTH - 20, COMPONENT_HEIGHT);
Dimension buttonDimension = new Dimension(BUTTON_WIDTH, COMPONENT_HEIGHT);
JLabel display = new JLabel(); // 숫자 값 및 결과 출력 화면
CalcGUIV1() {
super("CalcGUIV1");
calculator = new Calculator();
setSize(WINDOW_WIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT);
Font labelFont = display.getFont();
display.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
display.setFont(new Font(labelFont.getName(), Font.PLAIN, COMPONENT_HEIGHT - 5));
display.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(displayDimension));
setResizable(false);
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add(getDisplayPanel(), BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(getButtonPanel(), BorderLayout.CENTER);
clear();
}
public JPanel getDisplayPanel() {
JPanel displayPanel = new JPanel();
displayPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER));
displayPanel.setComponentOrientation(ComponentOrientation.RIGHT_TO_LEFT);
displayPanel.setPreferredSize(displayDimension);
displayPanel.add(display);
return displayPanel;
}
public JPanel getButtonPanel() {
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(5,3,10,5));
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
buttons[i] = new NumberButton(calculator, this);
buttons[i].setText(buttonText[i]);
buttons[i].setPreferredSize(buttonDimension);
buttons[i].addActionListener(this);
buttonPanel.add(buttons[i]);
}
for (int i = 10; i < 14; i++) {
buttons[i] = new ArithmeticOperatorCommandButton(calculator);
buttons[i].setText(buttonText[i]);
buttons[i].setPreferredSize(buttonDimension);
buttons[i].addActionListener(this);
buttonPanel.add(buttons[i]);
}
buttons[14] = new EqualCommandButton(calculator, this);
buttons[14].setText(buttonText[14]);
buttons[14].setPreferredSize(buttonDimension);
buttons[14].addActionListener(this);
buttonPanel.add(buttons[14]);
return buttonPanel;
}
public void showText(String text) { display.setText(text); }
public void clear() {
display.setText("0");
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (e.getSource() instanceof CommandButton) {
CommandButton cmdButton = (CommandButton) e.getSource();
cmdButton.execute();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CalcGUIV1 c = new CalcGUIV1();
c.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
c.setVisible(true);
}
}
package CommandPattern;
public class Calculator {
int operand1;
int operand2;
boolean operand1Set; // 첫 번째 피연산자(operand1) 값이 지정되었는지 확인
boolean operand2Set; // 두 번째 피연산자(operand1) 값이 지정되었는지 확인
boolean operatorSet; // 연산자가 지정되었는지 확인
char operator; // 연산자 저장
Calculator() {
clearFlags();
}
public void clearFlags() {
operand1Set = false;
operand2Set = false;
operatorSet = false;
}
public int getOperand1() {
return operand1;
}
public void setOperand1(int operand1) {
this.operand1 = operand1;
}
public int getOperand2() {
return operand2;
}
public void setOperand2(int operand2) {
this.operand2 = operand2;
}
public boolean isOperand1Set() {
return operand1Set;
}
public void setOperand1Set(boolean operand1Set) {
this.operand1Set = operand1Set;
}
public boolean isOperand2Set() {
return operand2Set;
}
public void setOperand2Set(boolean operand2Set) {
this.operand2Set = operand2Set;
}
public boolean isOperatorSet() {
return operatorSet;
}
public void setOperatorSet(boolean operatorSet) {
this.operatorSet = operatorSet;
}
public char getOperator() {
return operator;
}
public void setOperator(char operator) {
this.operator = operator;
}
}
package CommandPattern;
public interface Command {
public void execute();
}
package CommandPattern;
import javax.swing.*;
public abstract class CommandButton extends JButton implements Command {
private Calculator calculator;
public CommandButton(Calculator calculator) {
super();
this.calculator = calculator;
}
public Calculator getCalculator() { return calculator; }
@Override
public abstract void execute();
}package CommandPattern;
public class ArithmeticOperatorCommandButton extends CommandButton {
public ArithmeticOperatorCommandButton(Calculator calculator) {
super(calculator);
}
@Override
public void execute() {
if (getCalculator().isOperand1Set()) { // 첫 번째 피연산자 값이 지정되어야만 연산자 처리 가능
getCalculator().setOperator(getText().charAt(0));
getCalculator().setOperatorSet(true);
}
}
}package CommandPattern;
public class EqualCommandButton extends CommandButton {
CalcGUIV1 display;
public EqualCommandButton(Calculator calculator, CalcGUIV1 display) {
super(calculator);
this.display = display;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
int result = 0;
Calculator calculator = getCalculator();
if (calculator.isOperand1Set() && calculator.isOperand2Set() && calculator.isOperatorSet()) { // 두 개 피 연산자값과 연산자가 지정되었다면
int operand1 = calculator.getOperand1();
int operand2 = calculator.getOperand2();
char op = calculator.getOperator();
if (op == '+') {
result = operand1 + operand2;
}
else if (op == '-') {
result = operand1 - operand2;
}
else if (op == '*') {
result = operand1 * operand2;
}
else if (op == '/') {
result = operand1 / operand2;
}
}
display.showText("" + result);
calculator.clearFlags();
}
}package CommandPattern;
public class NumberButton extends CommandButton {
CalcGUIV1 display;
public NumberButton(Calculator calculator, CalcGUIV1 display) {
super(calculator);
this.display = display;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
Calculator calculator = getCalculator();
if (calculator.isOperand1Set() && calculator.isOperatorSet()) { // 첫 번째 피연산자와 연산자가 지정되었다면 두 번째 피연산자 값으로 사용
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(getText());
calculator.setOperand2(num2);
display.showText("" + num2);
calculator.setOperand2Set(true);
}
else { // 첫 번째 피연산자 값 지정
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(getText());
display.showText("" + num1);
calculator.setOperand1(num1);
calculator.setOperand1Set(true);
}
}
}'Java > 고급객체지향' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 고급객체지향 프로그래밍 - 템플릿 메소드 패턴(Template Method pattern) (0) | 2021.12.12 |
|---|---|
| 스테이트 패턴(State Pattern) (0) | 2021.12.12 |
| 고급객체지향 프로그래밍 - 퍼사드 패턴(Facade Pattern) (0) | 2021.12.12 |
| 고급객체지향 프로그래밍 - 어댑터 패턴(Adapter Pattern) (0) | 2021.12.12 |
| 고급객체지향 프로그래밍 - 다오 패턴(DAO Pattern) (0) | 2021.12.12 |